Bundler3 & Bundler2
Code
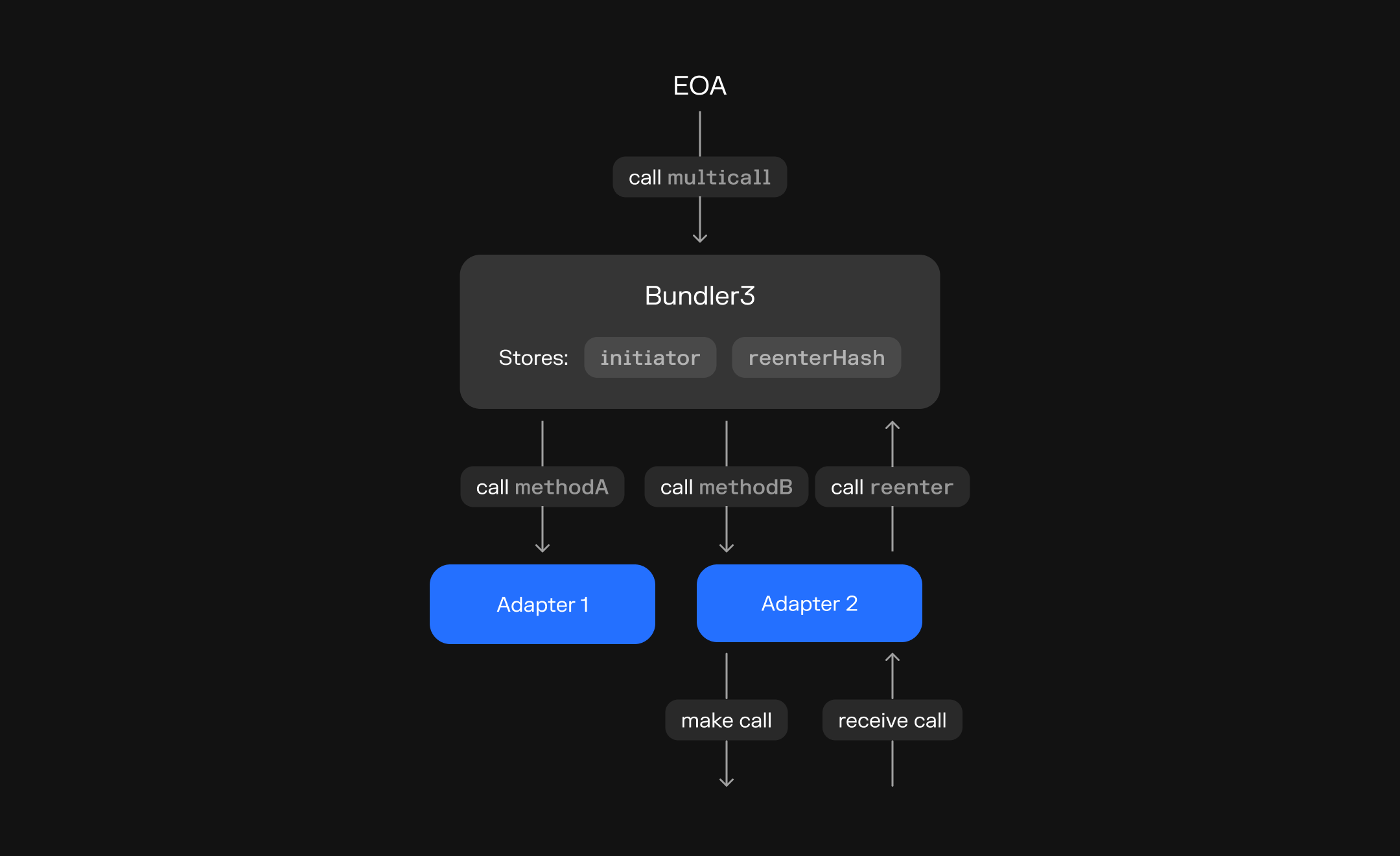
Bundler3 repository Bundler2 repositoryBundler3 Structure
-
The core
Bundler3contract implementsmulticall(Call[] calldata bundle), where each call is defined by:to: Target addressdata: Calldatavalue: Native currency amountskipRevert: Flag to skip reverting if this particular call failscallbackHash: Specifies the hash used for controlling reentrancy callbacks
-
Adapters all inherit from
CoreAdapter, which provides access to the initiator (the original caller) via transient storage. This mechanism allows adapters to enforce strict permission checks (e.g. only acting on behalf of the initiator). -
Chain-specific adapters, such as
EthereumGeneralAdapter1, extend the baseGeneralAdapter1to support network-specific features (e.g. stETH on Ethereum). -
Specialized adapters target specific integrations:
ParaswapAdapterfor DEX aggregation (buy/sell/swaps)- Migration adapters for moving user positions between protocols (Aave, Compound, Morpho, etc.)
Bundler2 Structure

-
All bundlers inherit from
BaseBundlerthat enables bundling multiple function calls into a singlemulticall(bytes[] calldata data)call to the end bundler contract. -
Each chain-specific bundler is available under its chain-specific folder (e.g.
ethereum). -
Some chain-specific domains are also scoped to the chain-specific folder because they are not expected to be used on any other chain (e.g. DAI and its specific
permitfunction is only available on Ethereum - seeEthereumPermitBundler. -
User-end bundlers are provided in each chain-specific folder, instantiating all the intermediary domain-specific bundlers and associated parameters (such as chain-specific protocol addresses, e.g.
EthereumBundler).
Permit 2
In November 2022, Uniswap Labs introduced Permit2, a robust token approval contract designed to standardize and secure token approvals across various smart contracts. By enabling signature-based approvals and efficient management of token allowances, Permit2 significantly enhances the user experience. It reduces transaction costs and bolsters smart contract security by mitigating risks associated with traditional approval methods.
The integration of Permit2 is set to benefit the entire DeFi ecosystem. Specifically, the Bundlers, operating within the Morpho V0, V1 and V2 frameworks, leverage Permit2's features to streamline transactions. This integration ensures more secure, cost-effective, and user-friendly operations across these platforms.
Discover the full potential of Permit2 and how it revolutionizes token approvals in the integration guide.

