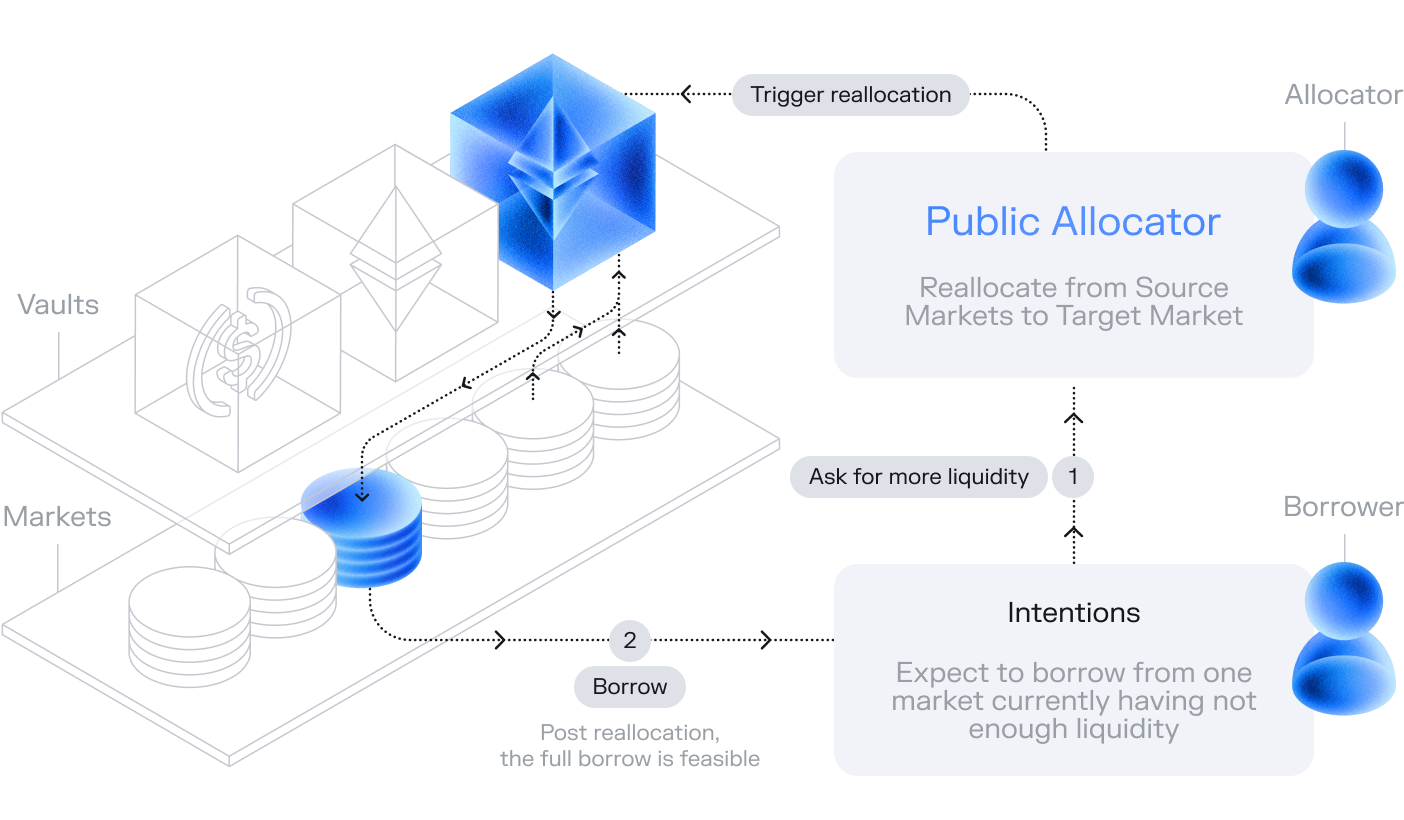
Public Allocator
The Public Allocator is a powerful onchain tool that solves liquidity fragmentation across isolated markets. For developers, it provides a mechanism to programmatically move liquidity on-demand, ensuring a user's borrow transaction can be fulfilled even if the target market initially has insufficient funds.
This creates a user experience similar to a single, deep liquidity pool while retaining the risk-isolated benefits of Morpho's market design.
Core Integration: reallocateTo
The primary function for interacting with the Public Allocator is reallocateTo. This function pulls assets from multiple source markets within a vault and supplies them to a single destination market in one atomic transaction.
Function Signature
function reallocateTo(
address vault,
Withdrawal[] calldata withdrawals,
MarketParams calldata supplyMarketParams
) external payable;Parameters
vault: The address of the MetaMorpho vault containing the liquidity.withdrawals: An array ofWithdrawalstructs, each specifying a source market and an amount to withdraw.supplyMarketParams: AMarketParamsstruct defining the single destination market where all withdrawn funds will be deposited.
Important Requirements
To successfully call reallocateTo, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Sorted Withdrawals: The
withdrawalsarray must be sorted in ascending order by market ID. - Pay the Fee: The transaction must be sent with the correct
feein gas token (E.g Ethereum: in ETH ) asmsg.value. You can query this fee by calling thefee(vaultAddress)view function on the Public Allocator contract. Note: This fee is set and collected by the vault curator, not by Morpho. The curator can set it to 0. - Respect Flow Caps: The withdrawal and supply amounts must not exceed the
maxOutandmaxInflow caps configured by the vault curator for each market. - Valid Markets: All source and destination markets must be enabled in the vault's configuration.
- No Self-Supply: The destination market (
supplyMarketParams) cannot be included in thewithdrawalsarray.
Example: Solidity Integration
Here is a simplified example of how you might construct and call reallocateTo within a smart contract.
// Assuming IPublicAllocator and IMetaMorpho interfaces are available
IPublicAllocator publicAllocator = IPublicAllocator(PA_ADDRESS);
IMetaMorpho vault = IMetaMorpho(VAULT_ADDRESS);
// 1. Check prerequisites
require(vault.isAllocator(address(publicAllocator)), "PA: Not an allocator");
uint256 requiredFee = publicAllocator.fee(address(vault));
// 2. Prepare withdrawal parameters (must be sorted by market ID)
Withdrawal[] memory withdrawals = new Withdrawal[](2);
// Withdrawal from Market A (e.g., Idle Market)
withdrawals[0] = Withdrawal({
marketParams: marketAParams, // MarketParams for Market A
amount: 70 * 1e18
});
// Withdrawal from Market B (e.g., wstETH Market)
// The ID of Market B must be greater than the ID of Market A
withdrawals[1] = Withdrawal({
marketParams: marketBParams, // MarketParams for Market B
amount: 800 * 1e18
});
// 3. Define the destination market
MarketParams memory supplyMarketParams = rETHMarketParams; // MarketParams for rETH Market
// 4. Execute the reallocation
publicAllocator.reallocateTo{value: requiredFee}(
address(vault),
withdrawals,
supplyMarketParams
);Recommended Integration Flow
For a robust dApp integration, the onchain reallocateTo call should be the final step in a flow that uses offchain data to ensure success.
1. Check Target Market Liquidity
First, check if the user's borrow can be fulfilled by the target market's existing liquidity. If so, no reallocation is needed.
2. Query for Reallocatable Liquidity
If more liquidity is required, use the Morpho API to query the publicAllocatorSharedLiquidity for the target market. This will return a list of all source markets across all vaults that can provide liquidity.
3. Simulate and Build Transaction
Using the data from the API, construct the withdrawals array. It is highly recommended to use the Morpho SDKs to simulate the transaction before asking the user to sign. This verifies that flow caps are respected and the call will succeed.
4. Bundle and Execute
For the best user experience, bundle the reallocateTo call with the user's borrow call into a single transaction using a Morpho Bundler. This ensures atomicity: if the reallocation fails, the entire operation (including the borrow) reverts, preventing failed transactions for the user.
Key Resources
| Resource | Link | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Step-by-Step Tutorial | /build/borrow/tutorials/public-allocator/ | A practical guide on how to trigger a reallocation, including an Etherscan walkthrough. |
| Contract Addresses | /get-started/resources/addresses/ | Official addresses for the Public Allocator contract on all supported chains. |
| Solidity Specs & Errors | /get-started/resources/contracts/public-allocator/ | Detailed contract specifications, function descriptions, and a table of common error messages. |
| API & Data Endpoints | /tools/offchain/api/ | How to query GraphQL for flow caps, fees, and available reallocatable liquidity. |

